Tuesday, February 28, 2023
Selecting the right peristaltic pump head can be a challenging task but we are here to make it easy. Just contact us and we will do the heavy lifting for you.
If you would prefer to learn more about the selection process for peristaltic pump head read on.
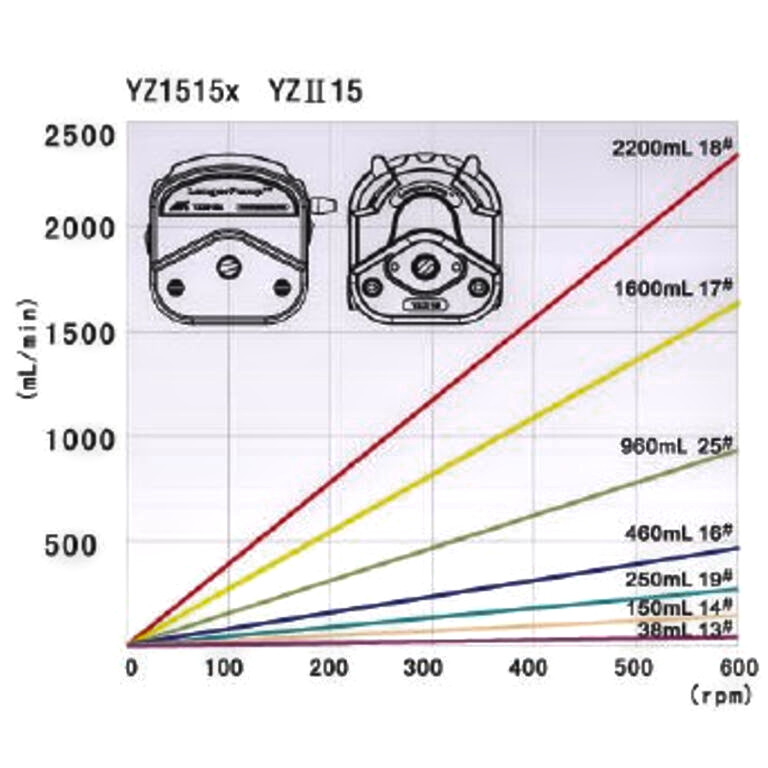
The flow rate in a peristaltic pump head is proportional to the rotational speed of the drive, measured in RPM. The flow rate per revolution varies depending on the inside diameter of the tubing. For instance, at 600 RPM, a pump head with 18# size tubing delivers 2200ml/min, while one with 16# tubing delivers 460ml/min at the same speed.
Comparing flow rates for different tubing sizes
A correction factor may be applied to account for variables such as suction and discharge pressure, tubing material, viscosity, and temperature of the medium.
By using the spreadsheet provided in the link, the calculation of flow rate can be automated, significantly expediting the process.
Running a peristaltic pump at its maximum speed for an extended period of time is not advisable as it can potentially decrease the lifespan of the pump head. Hence, it is recommended to operate the pump head at lower speeds to ensure its longevity. Top speed of most peristaltic pump heads is 600RPM.
To extend the life of both the tube and the pump head, it is advisable to operate the peristaltic pump at lower speeds. This is particularly important when pumping high viscosity fluids, as lower speeds can help achieve the desired flow rate.
Typically, the pressure rating is around 2 bar, but it is possible to achieve a higher pressure of up to 16 bar with specialized tubing and design.
In general, peristaltic pump tubing is highly sensitive to increased discharge pressure, which can significantly decrease its lifespan. Elevating the discharge pressure to 2 bar may cause an 80% reduction in tube life.
The peristaltic pump head is designed for a constant flow rate and typically features 2-3 rollers to maximize flow per revolution. More rollers will result in smaller flow rates but decreased pulsation. The rollers, rotor, and body can be optimized for cost reduction while maintaining performance.
Dispensing pump heads, on the other hand, vary in accuracy depending on the application. They typically feature a larger number of rollers and an offset roller design to increase accuracy. The body is manufactured to tighter tolerances. Peristaltic pumps can achieve accuracy as high as 0.2% with the correct tubing.
There are various methods to load tubing into a peristaltic pump, including the easy load mechanism and fixed track. The easy load mechanism utilizes a lever to load and lock the tubing in the pump head, while the fixed track method involves feeding the tubing through a track, which allows for more loading cycles. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the user's priorities.
Peristaltic pump tubing typically comes in two common wall thicknesses: 1.6mm and 2.4mm. The thicker wall tubing is recommended for pumping more viscous substances or when higher burst pressures are expected.
A benefit of peristaltic pumps is their ability to function as pinch valves, preventing fluid from flowing back through the tubing.
Using peristaltic pumps as pressure relief valves can be a complex and challenging task and is not recommended but is achievable.
While most peristaltic pump heads have fixed tracks, there are models that incorporate springs, providing several advantages such as reducing tubing occlusion force and wear. The spring mechanism can act as a cushioning effect on the tubing, prolonging its life.
Tube clamps are devices used to hold the tubing in place and prevent it from being fed through a rotating pump head. These clamps can be adjusted manually or automatically. Tube stops, on the other hand, are placed on the tubing to prevent it from being fed through the pump head in certain designs that do not require tube clamps.
A tube element is a piece of tubing that has connectors on both ends, which simplifies loading and reduces user error. However, this convenience can increase the cost of the peristaltic pump and the connectors will come in contact with the substance being pumped.
Tube fitting assembly and tubing clamper
When pumping chemically aggressive substances the material should be resistant in case of tube failure and the substance spilling out.
Yes, there are quieter and louder peristaltic pump heads. The noise level of a peristaltic pump head can depend on various factors such as the quality of the design of the pump head and the type of tubing used. It's important to consider the noise level when choosing a peristaltic pump, especially in settings where noise may be a concern such as laboratories or medical facilities.
The drain plug in a peristaltic pump head is a small opening at the lowest point of the pump head. It is used to drain any fluid accumulated in the pump head, which can occur during tube failure.
It’s a term used to quantify how many times roller will occlude peristaltic pump tubing. More occlusions per minute shorter tube life.
It’s a tool developed by PCT. The spreadsheet linked below offers a flow rate calculator that enables you to quickly and accurately calculate the flow rate of your peristaltic pump.
By entering the drive speed, the calculator provides the flow rate for water at 21 C with silicon tubing and virtually zero suction and discharge conditions.
It's important to note the maximum speed of your peristaltic pump. If you input your target flow rate, you'll receive a list of all available pump-heads along with the required pump speed to achieve the desired flow rate.
The calculator also helps you estimate tube life by inputting the flow rate and time, which provides the total number of roller passes.
Additionally, you can use the tool for dispensing by entering the volume and time you wish to dispense, and it will provide a list of pump-heads, corresponding tubing, and pump speed needed to achieve the desired dispensing.
As a general rule of thumb, increasing the aspect ratio of the tubing wall to the inside bore can increase tube life, although this is an oversimplification.
The Benefits of Coriolis Meter-Pump Systems Compared to Legacy Solutions
If you need any assistance in choosing the correct pump head please feel to get in touch with our expert engineers at sales@pctflow.com or call 01953 609930.
PCT are a leading UK distributor and your enquiry will be handled with the utmost professionalism. Please provide your details below.